SUSTAINABILITY
INVESTING
Rs. 2 Bn
IN THE DFCC GREEN BOND

WATER
CONSUMPTION
2024
24,716 Liters
2023
23,704 Liters

REFORESTATION OF THE
RAJAWAKA FOREST RESERVE
Rs. 5.7 Mn
TOTAL INVESTMENT

SOLAR ENERGY
GENERATED
2024
1,108 Mwh
2023
1,001 Mwh
LITRES OF
RAINWATER HARVESTED
2024- 2.9 Mn
2023- 2.9 Mn
NO OF TREES SAVED
2024
5,824
2023
4,313

E-WASTE
2024
2,850Kg
2023
330 Kg
ELECTRICITY CONSUMPTION
2024
1440 Mwh
2023
1479 Mwh

TOTAL SOLAR
INVESTMENT
2024
Rs. 26 Mn
2023
3- Rs. 26.8 Mn
PAPER REDUCTION
2024
12%
2023
33 %
281
EMPLOYEE PARTICIPATING IN VARIOUS ENVIRONMENTAL INITIATIVES
TOTAL NUMBER OF GREEN BUILDING 30
CARBON FOOTPRINT REDUCTION
7.3%

ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY
In view of climate change and the scarcity of resources, as well as their current and potential impact on surrounding communities, this pillar represents our commitment towards environmental sustainability that transcends beyond business. As an organisation built on a mission of driving sustainable, responsible and profitable growth, we consistently strive towards minimising our carbon footprint and optimising resources, while contributing towards the restoration of vital ecosystems in Sri Lanka.
Our Approach to Environmental Sustainability
Governance:
Key Challenges:
Escalating costs and the shortage of resources and materials continued to impact operations and minimise the potential for expansion. The impacts of climate change continue to manifest at an alarming rate, with increasing global temperatures, record-high greenhouse gas levels, and extreme weather events potentially impacting businesses and communities across the island.
ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY
-
A growing green building network and investments in renewable energy.
A strong brand reputation for sustainable initiatives, and an ongoing integration of climate risk mitigation to build organisational resilience.
Adoption of green office initiatives and digitisation to drive the optimised use of resources.
First life insurer to pioneer investment in a Green Bond, taking on an anchor role in sustainable financing.
Achieving cost savings through effective energy optimisation strategies.
STRENGTHS
-
Non-availability of green insurance products.
Dependence on third-party suppliers with varying sustainability standards.
Challenges gathering data for calculating the carbon footprint.
WEAKNESSES
-
Potential for climate risk-based insurance products, and the introduction of policies that promote sustainability amongst stakeholders.
Government and regulatory support for green financing initiatives.
Expanding sustainable investment portfolios to attract ESG conscious investors.
Enhanced brand image and Company reputation.
Improvement in stakeholder confidence.
OPPORTUNITIES
-
Competitive pressure from companies with stronger environmental commitments.
Potential carbon tax implications in the future
An increased exposure to climate- related risks (e.g., natural disasters affecting mortality) and affecting insurance claims and underwriting.
Non-availability of carbon pricing policies in Sri Lanka for carbon credit programs and Cap-and-Trading system on total GHG emissions.
Increased frequency of natural disasters impacting actuarial models and pricing.
Risk of greenwashing accusations if insurers fail to meet sustainability claims.
THREATS

HEAR FROM OUR LEADERSHIP:

E. T. L. RANASINGHE
Managing Director/Chief Executive Officer
-
The outcomes of environmental sustainability and responsible practices have profound implications for our stakeholders. At Ceylinco Life, we prioritize stakeholder needs and adhere to the highest standards of excellence, ensuring we uphold globally recognized principles and maintain our reputation as a responsible corporate entity. Our ability to navigate the evolving regulatory landscape and meet market expectations strengthens stakeholder confidence.
Climate change and related insurance risks are growing concerns in Sri Lanka, particularly regarding natural disasters and extreme weather events. As an insurance company with a long-term growth perspective, our purpose is to protect ourselves and our stakeholders from potential risks. We engage in various climate change mitigation strategies to safeguard our future.
Sustainable practices, such as green investments and eco-friendly initiatives, ensure long-term financial stability. These commitments enable us to deliver value and support the community and future generations for years to come. -
While Sri Lanka has several environmental regulations, the insurance sector lacks clear guidelines for integrating ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) factors into risk assessments and operations. Additionally, high implementation costs and limited financial resources pose challenges for businesses.
Promoting environmentally friendly policies and initiating renewable energy projects, water recycling, wastewater management, and sustainable investments face obstacles due to the market's lack of knowledge and capabilities. At Ceylinco Life, we have overcome these challenges through our relentless commitment.
Although the transition to renewable energy and other sustainable investments helps mitigate climate change impacts, more momentum is needed to bridge the gap in terms of necessary expertise, affordability, and sourcing of required materials and resources. We understand the issues and implications of climate change pose challenges to our operations and believe strengthening disaster preparedness and risk management functions is crucial for building organizational resilience and successfully meeting these challenges. -
The rise of natural disasters and supply chain disruptions is driving a shift towards sustainable and low-carbon economies. This will require stricter regulations, increased reporting requirements, and evolving consumer preferences. The financial and investment sectors are expected to undergo significant transformation due to digitalization and workforce development. Ceylinco Life is addressing these impacts by integrating sustainable practices, investing in green technologies, and fostering environmental responsibility to navigate climate change challenges.
-
Ceylinco Life is dedicated to integrating sustainable practices across all aspects of our operations, with the ambitious long-term goal of achieving Net-Zero Carbon Emissions. We are committed to consistently reducing our greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 5% year-on-year. Our comprehensive strategy encompasses every facet of our business and is detailed extensively throughout this report. For more information, please refer to pages 153-166 of this report.
-
The Company takes a strong stance against greenwashing by prioritizing transparency, authenticity, and verifiable environmental data in its disclosures. We are committed to long-term sustainability goals, supported by third-party audits and measurable outcomes, ensuring all claims are based on clear, actionable metrics. Regular engagement with stakeholders allows us to gather feedback and adopt practices in line with evolving global standards. By aligning with recognized frameworks and embedding sustainability across our operations, we foster a culture of continuous improvement and accountability, building trust with customers, investors, and regulators.
ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY

Progress in 2024:
The construction of the Nittambuwa Green Building has commenced and is expected to reach completion by the end of 2025.
All ground preparations were completed for the construction of another Green building in Ambalantota, which will expect to commence on January 14, 2025.
The Company invested in its second-largest solar system at the Investment Building in the Park Street Building (Ceylinco Healthcare Centre), with a capacity of 80 kW. Additionally, a 10 kW solar system was installed in Matugama, while the 15 kW solar powered system in the Nugegoda building was connected to the grid, thereby transforming it into a green building.
We investigated one of the high electricity-consuming branches, Kotahena, and made modifications in the customer area to optimize the use of the air conditioning system. As a result, we achieved a reduction of approximately 3,000 units per month, which is about a 33% decrease in energy consumption.

Green buildings
in the branch network



Scan the QR code
to view the stone
laying ceremony of
the Ambalantota
and Nittambuwa
branches


Green buildings
of buildings are fully powered by solar energy
Saved through Solar Generation
New Green building projects initiated
Solar Generation
Emissions avoided through Solar
Trees saved through Solar
The Company employs the 6Rs of resource management across its operations, to ensure that the following vital resources are preserved, managed, and optimised:
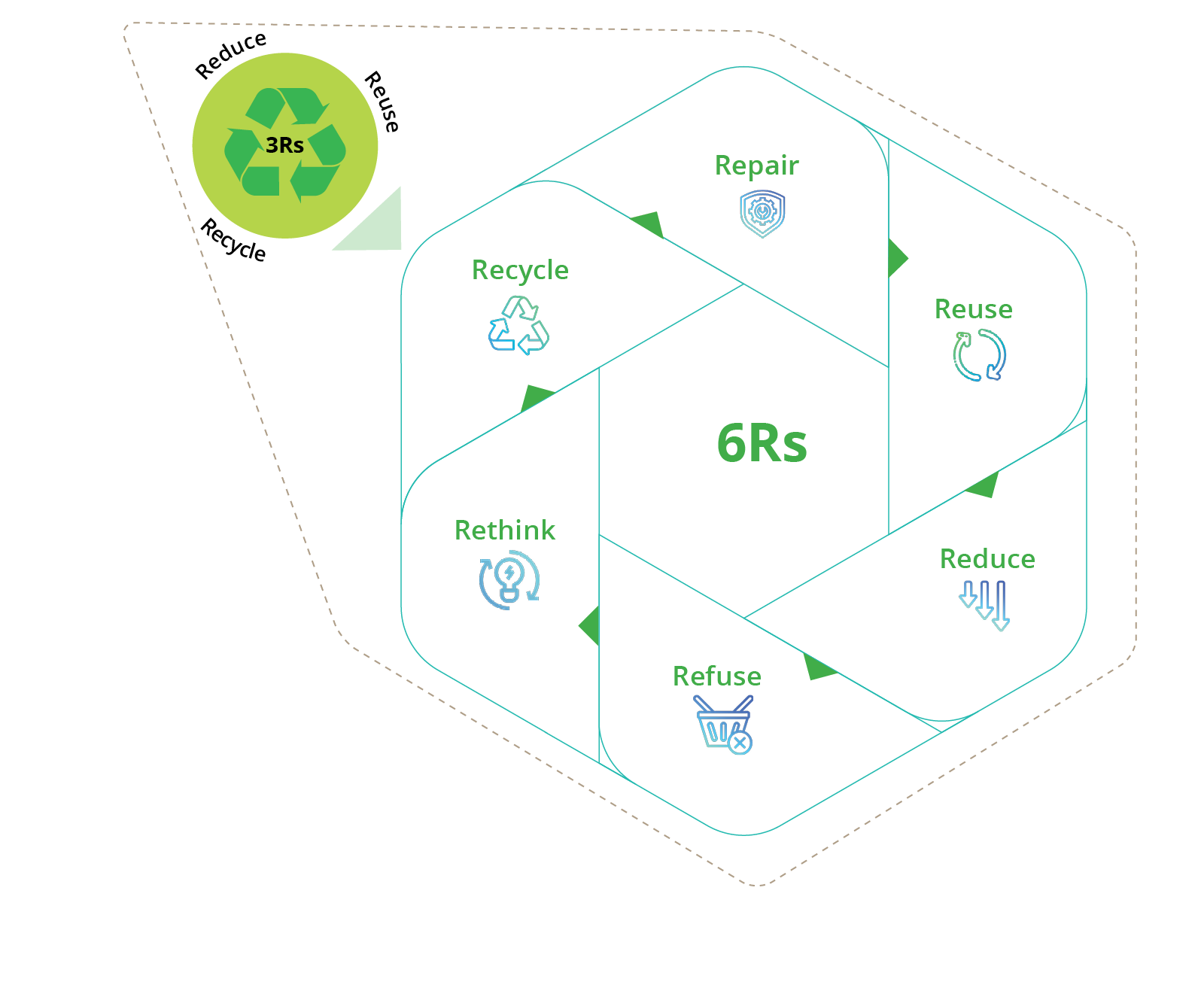


Environmental Sustainability
Resource Management at a Glance




Rs. 26 Mn
Solar investment
1108 MWh
Solar power generated
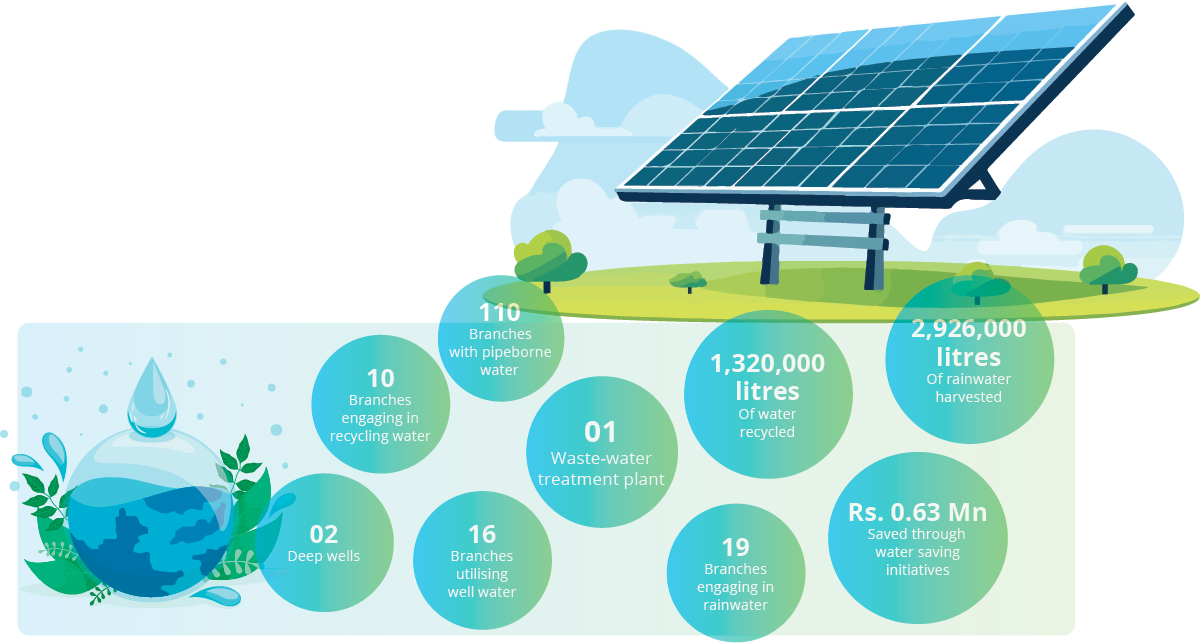
Water Consumption






During the year, the Company conducted an e-waste campaign, with 65 employees. 2,850 Kg of e-waste was collected and disposed with the support of an accredited third-party recycler.


16 No of branches including Own Buildings Nelliady, Jaffna, Wennappuwa, Mount Lavinia, Minuwangoda and Matugama branches utilise well water. Ceylinco Life did not record any incidents of waterbodies being negatively affected by water runoffs and no hazardous or harmful discharges took place during the year.
All forms of waste, constituting e-waste, food waste, and paper waste are disposed of via local authorities and authorised third-party recyclers.
Environmental Sustainability

Climate Action and Ecosystem Conservation
The reforestation project in Rajawaka, Balangoda, spans 10 acres and involves planting 10,000 trees. This initiative is designed to combat the adverse effects of climate change by enhancing carbon sequestration, restoring biodiversity,
Reforestation of the Rajawaka Forest Reserve
Project Partner: Rainforest Protectors of Sri Lanka
Objective: The restoration of the Rajawaka Forest Reserve area in Balangoda, which is surrounded by mountains, grass, shrubland, and catchment blocks and lies on the edge of the wet and intermediate zones. Over the years, man-made fires have damaged the natural environment, resulting in its degradation.
3 years
project duration
10 Acres
to be restored
5,000 trees
planted to date
Rs. 5.7 Mn
total investment


Anticipated Environmental Outcomes:
- Improving and enhancing the catchments enabling water security
- Decreasing frequency of fires and increasing fire resistance
- Increasing biodiversity by planting 50 species of native trees
- Improving soil fertility and microorganism activity
- Restoring pollinator habitats (bees, hornets)
- Producing long-term carbon benefits
- Providing education on conservation
- Improving forest cover in the area
Beach Clean-up Programmes
Project Partner: Clean Ocean Force
Objective: Collection and responsible disposal of harmful pollutants and trash
across segments of Sri Lanka’s coast.
Locations: Beach area in Mattakkuliya and Akkarai
2
Programmes conducted
152
Employees participated
41
Other participants
600 kg
of waste collected
Anticipated Environmental Outcomes:
- Raising awareness on marine pollution
- Helping protect marine biodiversity
- Preventing waste from entering oceans
- Increasing tourism appeal
- Demonstrating responsible corporate action





Akkarai beach, Atchuveli and Mattakkuliya Beach
Climate Change Mitigation
Ceylinco Life believes climate risks are material to its operations, and therefore has employed the following strategies to mitigate the impact of climate change. Climate change is a medium to long-term risk, with a complex quantification of impacts on our activities. Ceylinco Life’s strategy is not only to adapt, but also to take advantage of its expertise to provide solutions.
Carbon 5% Down Challenge
“We are committed to reducing our Carbon Footprint (CFP) by 5% annually as part of our long-term strategy to achieve net-zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions across our entire business by 2050.”
Double materiality related to Climate Related Risks and Opportunities
Financial Materiality
Focuses on how climate risks impact the Company’s financial position and enterprise value and expected to influence decisions of the primary users of the financial report.
Reporting Framework: SLFRS S1 & S2

Environment and Social Materiality
Focuses on how the Company’s actions impact the environment, society, and climate.
Reporting Framework: GRI
Pioneering Climate Action through Innovation and Responsibility
Sustainable Investment Practices
- Engage in green investments by allocating funds to renewable energy projects, sustainable infrastructure, and climate-resilient initiatives.
- Discourage investment exposure to carbon-intensive industries such as coal and oil.
(What Ceylinco Life Did)
Investing Rs. 2 Bn in the DFCC Green bonds
Climate-Responsible Underwriting
- Develop underwriting guidelines that prioritise and consider climate related risk factors into consideration.
- Refer to the ESG Roadmap for 2024-2028 (Page 32) for initiatives in this regard
Operational Sustainability
(What Ceylinco Life Did)
- Achieve a carbon reduction of 5% y-o-y.
- Renewable energy for office facilities. Installation of solar panels in all the green buildings.
- Promote responsible electronic waste disposal through an annual e-waste campaign.
- Assessing the financial impact of floods in 2024 and developing an action plan to mitigate business losses.
- Refer to pages 36–37 for more details
Engagement and Advocacy
- Actively collaborating with industry peers, employees, and ESG experts to promote climate policies and resilience initiatives.
- Advocate for stronger regulatory frameworks to support the transition to a sustainable economy.
(What Ceylinco Life Did)
- Stakeholder engagement activities by the Green Club
- Participation at the EY annual ESG Sustainability event and bringing down the expertise from EY Malaysia
- Partnered with the Department of Forest Conservation for a 10-acre reforestation project
Climate Resilience and Adaptation
(What Ceylinco Life Did)
- Partner with communities and organisations to support climate adaptation projects and offer financial solutions to help mitigate the effects of natural disasters and promote recovery.
Customer Awareness and Education
(What Ceylinco Life Did)
- Launch awareness campaigns to educate policyholders on the impacts of climate change.
Transparency and Reporting
- Launching a fund to support reforestation in food-prone areas, reducing disaster risks for local communities.
- Publish climate-related disclosures in alignment with Sustainability related accounting standards (S1,S2) and GRI framework.
- Establish measurable KPIs to track performance against climate commitments.
Governance and Accountability
- Assign accountability for climate strategy to the ESG Committee (Sub Board Committee).
- Establish a dedicated Climate Task Force and ESG subcommittee for implementation and progress.
- Engage employees across all levels through training and initiatives to embed climate awareness into Company culture.
(What Ceylinco Life Did)
- Addressing the importance of environment sustainability and preservation at the employee onboarding process.
GHG Emissions
Ceylinco Life conducted a comprehensive assessment of its GHG emissions in accordance with the ISO 14064-1:2018 standard. All GHG emissions were reported as tonnes of CO2 equivalent (tCO2e).
Total emissions 2024 vs 2023
| SCOPE | 2024 (tCO2e) | 2023 (tCO2e) | YOY % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope 01 | 247.74 | 320.27 | -22.6 |
| Scope 02 | 616.22 | 634.14 | -2.8 |
| Scope 03 | 1,999.18 | 2,134.22 | -6.3% |
| Total | 2,863.14 | 3,088.63 | -7.3% |

Scope 01 – Direct greenhouse gas emissions that occur from sources that are owned or controlled by an entity
| Source | 2024 (tCO2e) | 2023 (tCO2e) | YOY Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business travel (Company Owned Vehicles) | 142.58 | 133.58 | 6.7% |
| Diesel Generators | 3.25 | 10.80 | -69.9% |
| Employee Commuting, paid by the Company | 69.54 | 89.55 | -22.35% |
| Refrigerant Leakage | 31.49 | 89.50 | -63.17% |
| Fire Extinguishers | 0.36 | 0.47 | -23.4% |
| LP Gas | 0.52 | 0.37 | -40.5% |
| Total | 247.74 | 320.27 | -22.6% |
Scope 02 – Indirect greenhouse gas emissions from the generation of purchased or acquired electricity, steam, heating or cooling consumed by an entity
| Source | 2024 (tCO2e) | 2023 (tCO2e) | YOY Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electricity | 616.22 | 634.14 | -2.8% |
Scope 03 – Indirect greenhouse gas emissions (not included in Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions) that occur in the value chain of an entity, including both upstream and downstream emissions
| Source | 2024 (tCO2e) | 2023 (tCO2e) | YOY Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employee Commuting, not paid by the Company | 1,916.69 | 2,007.19 | -4.5% |
| Transmission and Distribution Loss | 63.19 | 61.10 | 3.4% |
| Waste Disposal | 8.17 | 53.49 | -84.7% |
| Municipal Water | 3.70 | 3.60 | 2.7% |
| Business Air Travels | 6.35 | 7.45 | -14.8% |
| Freight road transport | 1.08 | 1.39 | -22.3% |
| Total | 1,999.18 | 2,134.22 | -6.3% |
SLFRS S2 transition provisions applied for financial emission C4(b) “an entity is not required to disclose its Scope 3 greenhouse gas emissions (see paragraph 29(a)) which includes, if the entity participates in asset management, commercial banking or insurance activities, the additional information about its financed emissions”
Ceylinco Life firmly believes that collaboration drives results, and therefore engages with a wide range of stakeholder groups to ensure broad-based participation and awareness on environmental sustainability.
Environmental Integration
Beginning from the Board, all staff members are involved in leading, planning, executing and supporting environmental initiatives. The Green Club spearheads ground-level initiatives and trains staff on sustainability standards.
22
Green Club Members
281
Employees participating in various environmental initiatives
Building Management and Supervision
Building supervisors are held responsible for making sure
that all owned facilities are in compliance with applicable
rules and regulations.
Across all branches, employees from each department are
assigned to monitor electricity consumption in compliance
with predetermined standards.
32
Building Supervisors
175
Employees to monitor electricity usage
Paperless Operations
The Company’s focus on digitalisation has significantly reduced paper usage and encouraged customers to adopt environmentally responsible practices.
3,728
Policyholders onboarded digitally
12,134
Active users of the customer App
Refer to page 159 for more details
Green Building Construction
Collaborates with suppliers to source eco-friendly materials, develop efficient designs, and adopt green construction practices to enhance sustainability and supply chain resilience.

Seed Donation Programme
Please refer to page 114 for the future outlook with respect to building resilient communities.
Seed donation programmes were conducted in selected Vaidiya Hamuwa health programmes to support ecosystems and food security.
Locations: Aralaganwila, Dehiattakandiya, Neluwa, Deniyaya
04
Seed donation programmes
818
Seed packets distributed
